Drupal 8 में कॉन्फ़िगरेशन ऑब्जेक्ट प्रकार बनाना
यह पेज Drupal 8 के लिए प्रशासनिक प्रबंधन पेजों के साथ एक कॉन्फ़िगरेशन ऑब्जेक्ट प्रकार बनाने का उदाहरण प्रस्तुत करता है। सरल कॉन्फ़िगरेशन और कॉन्फ़िगरेशन ऑब्जेक्ट्स की अवधारणाओं को समझने के लिए देखें https://drupal.org/node/2120523।
नीचे दिए गए कोड को शामिल करने वाले उदाहरण मॉड्यूल को सक्षम करने के बाद, कॉन्फ़िगरेशन फ़ॉर्म का उदाहरण «admin/config/system/example» पर उपलब्ध होना चाहिए, जैसा कि स्क्रीनशॉट में दिखाया गया है:
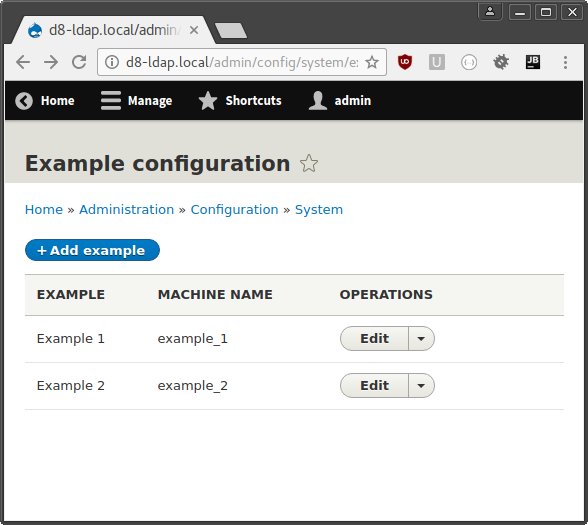
मॉड्यूल सेटअप और एडमिन मेन्यू में एंट्री
example/example.info.yml
name: Example description: 'Manages example configuration.' package: Example type: module core: 8.x
राउटिंग
(देखें कुछ सहायक क्लासेस जो entity paths के साथ काम करने के लिए जोड़े गए हैं, यह जानने के लिए कि इसे कैसे सरल बनाया जाए।)
example/example.routing.yml
routing.yml फ़ाइल प्रबंधन पेजों के लिए रूट्स परिभाषित करती है: सूची, जोड़ना, संपादित करना, हटाना।
entity.example.collection:
path: '/admin/config/system/example'
defaults:
_entity_list: 'example'
_title: 'Example configuration'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer site configuration'
entity.example.add_form:
path: '/admin/config/system/example/add'
defaults:
_entity_form: 'example.add'
_title: 'Add example'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer site configuration'
entity.example.edit_form:
path: '/admin/config/system/example/{example}'
defaults:
_entity_form: 'example.edit'
_title: 'Edit example'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer site configuration'
entity.example.delete_form:
path: '/admin/config/system/example/{example}/delete'
defaults:
_entity_form: 'example.delete'
_title: 'Delete example'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer site configuration'
example/example.links.menu.yml
यह कॉन्फ़िगरेशन -> सिस्टम पेज में लिंक जोड़ता है।
entity.example.collection: title: 'Example' parent: system.admin_config_system description: 'Configure example' route_name: entity.example.collection
example/example.links.action.yml
यह सूची पेज पर «जोड़ें» लिंक प्रदर्शित करता है।
entity.example.add_form:
route_name: 'entity.example.add_form'
title: 'Add example'
appears_on:
- entity.example.collection
ऑब्जेक्ट प्रकार क्लासेस
example/src/ExampleInterface.php
मान लेते हैं कि आपकी कॉन्फ़िगरेशन entity में properties हैं, तो आपको इंटरफ़ेस पर कुछ set/get मेथड्स परिभाषित करने की आवश्यकता होगी।
namespace Drupal\example;
use Drupal\Core\Config\Entity\ConfigEntityInterface;
/**
* Example entity को परिभाषित करने वाला एक इंटरफ़ेस प्रदान करता है।
*/
interface ExampleInterface extends ConfigEntityInterface {
// यहां अपनी कॉन्फ़िगरेशन प्रॉपर्टीज़ के लिए get/set मेथड्स जोड़ें।
}
example/src/Entity/Example.php
यह फ़ाइल कॉन्फ़िगरेशन entity क्लास को परिभाषित करती है।
namespace Drupal\example\Entity;
use Drupal\Core\Config\Entity\ConfigEntityBase;
use Drupal\example\ExampleInterface;
/**
* Example entity को परिभाषित करता है।
*
* @ConfigEntityType(
* id = "example",
* label = @Translation("Example"),
* handlers = {
* "list_builder" = "Drupal\example\Controller\ExampleListBuilder",
* "form" = {
* "add" = "Drupal\example\Form\ExampleForm",
* "edit" = "Drupal\example\Form\ExampleForm",
* "delete" = "Drupal\example\Form\ExampleDeleteForm",
* }
* },
* config_prefix = "example",
* admin_permission = "administer site configuration",
* entity_keys = {
* "id" = "id",
* "label" = "label",
* },
* config_export = {
* "id",
* "label"
* },
* links = {
* "edit-form" = "/admin/config/system/example/{example}",
* "delete-form" = "/admin/config/system/example/{example}/delete",
* }
* )
*/
class Example extends ConfigEntityBase implements ExampleInterface {
/**
* Example ID।
*
* @var string
*/
public $id;
/**
* Example लेबल।
*
* @var string
*/
public $label;
// यहां अपने विशेष कॉन्फ़िगरेशन प्रॉपर्टी get/set मेथड्स जोड़ें,
// इंटरफ़ेस को लागू करते हुए।
}
admin_permission key स्वचालित रूप से उन सभी उपयोगकर्ताओं को अनुमति देता है जिनके पास यह अनुमति है। यदि अधिक लॉजिक की आवश्यकता है, तो आप एक कस्टम एक्सेस कंट्रोलर निर्दिष्ट कर सकते हैं।
Drupal 8.6.x से शुरू होकर अनुशंसा की जाती है कि सभी कॉन्फ़िगरेशन ऑब्जेक्ट प्रकारों में अपनी annotations में config_export प्रॉपर्टी हो (देखें: https://www.drupal.org/node/2949023).
कॉन्फ़िगरेशन स्कीमा फ़ाइल
example/config/schema/example.schema.yml
example.example.*:
type: config_entity
label: 'Example config'
mapping:
id:
type: string
label: 'ID'
label:
type: label
label: 'Label'
example.schema.yml में \Drupal\example\Entity\Example में परिभाषित properties/attributes जोड़ें।
example.example.* एक कॉन्फ़िगरेशन वेरिएबल है, जो हमारे क्लास की properties/attributes को संदर्भित करता है, और आप अपनी entity के लिए “config_prefix” जोड़कर एक अलग वेरिएबल नाम निर्दिष्ट कर सकते हैं, उदाहरण के लिए:
@ConfigEntityType( .. ... config_prefix = "variable_name" ...
तब आप इसे इस प्रकार संदर्भित कर सकते हैं:
example.variable_name.*: ....
कॉन्फ़िगरेशन स्कीमा के बारे में अधिक जानकारी के लिए देखें कॉन्फ़िगरेशन स्कीमा/मेटाडेटा
Entity क्लासेस
example/src/Form/ExampleForm.php
namespace Drupal\example\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityTypeManagerInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Messenger\MessengerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\DependencyInjection\ContainerInterface;
/**
* Example add और edit फ़ॉर्म के लिए form handler।
*/
class ExampleForm extends EntityForm {
/**
* ExampleForm ऑब्जेक्ट बनाता है।
*
* @param \Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityTypeManagerInterface $entityTypeManager
* entityTypeManager।
*/
public function __construct(EntityTypeManagerInterface $entityTypeManager) {
$this->entityTypeManager = $entityTypeManager;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public static function create(ContainerInterface $container) {
return new static(
$container->get('entity_type.manager')
);
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function form(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$form = parent::form($form, $form_state);
$example = $this->entity;
$form['label'] = [
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => $this->t('Label'),
'#maxlength' => 255,
'#default_value' => $example->label(),
'#description' => $this->t("Example के लिए लेबल।"),
'#required' => TRUE,
];
$form['id'] = [
'#type' => 'machine_name',
'#default_value' => $example->id(),
'#machine_name' => [
'exists' => [$this, 'exist'],
],
'#disabled' => !$example->isNew(),
];
// अपनी कस्टम properties के लिए अतिरिक्त फ़ॉर्म एलिमेंट्स की आवश्यकता होगी।
return $form;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function save(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$example = $this->entity;
$status = $example->save();
if ($status === SAVED_NEW) {
$this->messenger()->addMessage($this->t('The %label Example created.', [
'%label' => $example->label(),
]));
}
else {
$this->messenger()->addMessage($this->t('The %label Example updated.', [
'%label' => $example->label(),
]));
}
$form_state->setRedirect('entity.example.collection');
}
/**
* हेल्पर फ़ंक्शन जो यह जांचता है कि Example कॉन्फ़िगरेशन entity मौजूद है या नहीं।
*/
public function exist($id) {
$entity = $this->entityTypeManager->getStorage('example')->getQuery()
->condition('id', $id)
->execute();
return (bool) $entity;
}
}
example/src/Controller/ExampleListBuilder.php
namespace Drupal\example\Controller;
use Drupal\Core\Config\Entity\ConfigEntityListBuilder;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
/**
* Example की सूची प्रदान करता है।
*/
class ExampleListBuilder extends ConfigEntityListBuilder {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function buildHeader() {
$header['label'] = $this->t('Example');
$header['id'] = $this->t('Machine name');
return $header + parent::buildHeader();
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function buildRow(EntityInterface $entity) {
$row['label'] = $entity->label();
$row['id'] = $entity->id();
// शायद यहां आपको कुछ और properties जोड़नी होंगी...
return $row + parent::buildRow($entity);
}
}
example/src/Form/ExampleDeleteForm.php
namespace Drupal\example\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityConfirmFormBase;
use Drupal\Core\Url;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
/**
* Example को हटाने के लिए फ़ॉर्म बनाता है।
*/
class ExampleDeleteForm extends EntityConfirmFormBase {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getQuestion() {
return $this->t('Are you sure you want to delete %name?', array('%name' => $this->entity->label()));
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getCancelUrl() {
return new Url('entity.example.collection');
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getConfirmText() {
return $this->t('Delete');
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$this->entity->delete();
$this->messenger()->addMessage($this->t('Entity %label has been deleted.', array('%label' => $this->entity->label())));
$form_state->setRedirectUrl($this->getCancelUrl());
}
}