Drupal 8-ում կոնֆիգուրացիոն օբյեկտի տիպի ստեղծում
Այս էջում ներկայացվում է օրինակ, թե ինչպես ստեղծել կոնֆիգուրացիոն օբյեկտի տիպ՝ ադմինիստրատիվ կառավարման էջերով Drupal 8-ի համար։ Պարզ կոնֆիգուրացիայի և կոնֆիգուրացիոն օբյեկտների մասին հասկացությունների ծանոթանալու համար դիտեք Https://drupal.org/node/2120523։
Նշված կոդով օրինակ մոդուլի միացմանց հետո կոնֆիգուրացիոն ֆորմայի օրինակ հասանելի կլինի «admin/config/system/example» հասցեում, ինչպես ցույց է տրված սքրինշոթում․
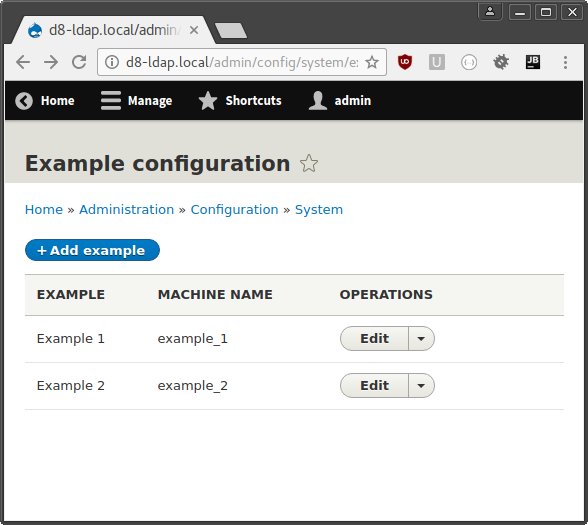
Մոդուլի կարգավորում և ադմինիստրատոր մենյուի մուտք
example/example.info.yml
name: Example description: 'Manages example configuration.' package: Example type: module core: 8.x
Մարսրուտավորում
(Դիտեք մի քանի լրացուցիչ դասեր, որոնք ավելացվել են էնթիթի ճանապարհների հետ աշխատելու համար՝ պարզելու, թե ինչպես դա հեշտացնել։)
example/example.routing.yml
routing.yml ֆայլը սահմանում է կառավարման էջերի մարսրուտները՝ ցանկ, ավելացում, խմբագրում, ջնջում։
entity.example.collection:
path: '/admin/config/system/example'
defaults:
_entity_list: 'example'
_title: 'Example configuration'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer site configuration'
entity.example.add_form:
path: '/admin/config/system/example/add'
defaults:
_entity_form: 'example.add'
_title: 'Add example'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer site configuration'
entity.example.edit_form:
path: '/admin/config/system/example/{example}'
defaults:
_entity_form: 'example.edit'
_title: 'Edit example'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer site configuration'
entity.example.delete_form:
path: '/admin/config/system/example/{example}/delete'
defaults:
_entity_form: 'example.delete'
_title: 'Delete example'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer site configuration'
example/example.links.menu.yml
Ավելացնում է հղում կոնֆիգուրացիայի էջին -> Սիստեմ
entity.example.collection: title: 'Example' parent: system.admin_config_system description: 'Configure example' route_name: entity.example.collection
example/example.links.action.yml
Այս դեպքում «Ավելացնել» հղումը հայտնվում է ցանկի էջում։
entity.example.add_form:
route_name: 'entity.example.add_form'
title: 'Add example'
appears_on:
- entity.example.collection
Օբյեկտների տիպերի դասեր
example/src/ExampleInterface.php
Եթե ձեր կոնֆիգուրացիոն էնթիթին կան հատկություններ, պետք է սահմանեք որոշ set/get մեթոդներ ինտերֆեյսում։
namespace Drupal\example;
use Drupal\Core\Config\Entity\ConfigEntityInterface;
/**
* Ապահովում է ինտերֆեյս, որը սահմանում է Example էնթիթի։
*/
interface ExampleInterface extends ConfigEntityInterface {
// Ավելացրեք ձեր կոնֆիգուրացիոն հատկությունների get/set մեթոդները այստեղ։
}
example/src/Entity/Example.php
Այս ֆայլը սահմանում է կոնֆիգուրացիոն էնթիթի դասը։
namespace Drupal\example\Entity;
use Drupal\Core\Config\Entity\ConfigEntityBase;
use Drupal\example\ExampleInterface;
/**
* Սահմանում է Example էնթիթը։
*
* @ConfigEntityType(
* id = "example",
* label = @Translation("Example"),
* handlers = {
* "list_builder" = "Drupal\example\Controller\ExampleListBuilder",
* "form" = {
* "add" = "Drupal\example\Form\ExampleForm",
* "edit" = "Drupal\example\Form\ExampleForm",
* "delete" = "Drupal\example\Form\ExampleDeleteForm",
* }
* },
* config_prefix = "example",
* admin_permission = "administer site configuration",
* entity_keys = {
* "id" = "id",
* "label" = "label",
* },
* config_export = {
* "id",
* "label"
* },
* links = {
* "edit-form" = "/admin/config/system/example/{example}",
* "delete-form" = "/admin/config/system/example/{example}/delete",
* }
* )
*/
class Example extends ConfigEntityBase implements ExampleInterface {
/**
* Example-ի ID-ն։
*
* @var string
*/
public $id;
/**
* Example-ի պիտակը։
*
* @var string
*/
public $label;
// Ձեր կոնֆիգուրացիոն հատկությունների get/set մեթոդները, որոնք պետք է իրականացնեք ինտերֆեյսը։
}
admin_permission բանալին ավտոմատ թույլ է տալիս այդ թույլտվությամբ բոլոր օգտվողներին մուտք ունենալ։ Եթե անհրաժեշտ է ավելի բարդ տրամաբանություն, կարող եք սահմանել սեփական մուտքի վերահսկիչ։
Drupal 8.6.x-ից սկսած խորհուրդ է տրվում, որ բոլոր կոնֆիգուրացիոն օբյեկտների տիպերը ունենան config_export հատկանիշ իրենց անոտացիաներում (տես՝ https://www.drupal.org/node/2949023)։
Կոնֆիգուրացիայի սկեմայի ֆայլ
example/config/schema/example.schema.yml
example.example.*:
type: config_entity
label: 'Example config'
mapping:
id:
type: string
label: 'ID'
label:
type: label
label: 'Label'
example.schema.yml-ում ավելացրեք հատկությունները/վճռորոշիչները, որոնք սահմանված են \Drupal\example\Entity\Example դասում։
example.example.*-ը կոնֆիգուրացիոն փոփոխականն է, որը հղում է մեր դասի հատկություններին/վճռորոշիչներին, և կարող եք նշել այլ փոփոխականի անուն ձեր էնթիթի համար՝ ավելացնելով «config_prefix»՝ օրինակ՝
@ConfigEntityType( .. ... config_prefix = "variable_name" ...
Այդ դեպքում կարող եք հղվել հետևյալ ձևով՝
example.variable_name.*: ....
Կոնֆիգուրացիայի սկեմայի վերաբերյալ ավելին կգտնեք Կոնֆիգուրացիայի սկեմա/մետատվյալներ էջում։
Էնթիթի դասեր
example/src/Form/ExampleForm.php
namespace Drupal\example\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityTypeManagerInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Messenger\MessengerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\DependencyInjection\ContainerInterface;
/**
* Հանդիսանում է Example-ի ավելացման և խմբագրման ֆորմայի հենակետը։
*/
class ExampleForm extends EntityForm {
/**
* ExampleForm օբյեկտի կոնստրուկտոր։
*
* @param \Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityTypeManagerInterface $entityTypeManager
* EntityTypeManager-ը։
*/
public function __construct(EntityTypeManagerInterface $entityTypeManager) {
$this->entityTypeManager = $entityTypeManager;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public static function create(ContainerInterface $container) {
return new static(
$container->get('entity_type.manager')
);
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function form(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$form = parent::form($form, $form_state);
$example = $this->entity;
$form['label'] = [
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => $this->t('Label'),
'#maxlength' => 255,
'#default_value' => $example->label(),
'#description' => $this->t("Label for the Example."),
'#required' => TRUE,
];
$form['id'] = [
'#type' => 'machine_name',
'#default_value' => $example->id(),
'#machine_name' => [
'exists' => [$this, 'exist'],
],
'#disabled' => !$example->isNew(),
];
// Ձեր հարմարեցված հատկությունների համար պետք կլինեն լրացուցիչ ֆորմայի դաշտեր։
return $form;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function save(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$example = $this->entity;
$status = $example->save();
if ($status === SAVED_NEW) {
$this->messenger()->addMessage($this->t('The %label Example created.', [
'%label' => $example->label(),
]));
}
else {
$this->messenger()->addMessage($this->t('The %label Example updated.', [
'%label' => $example->label(),
]));
}
$form_state->setRedirect('entity.example.collection');
}
/**
* Օգնող ֆունկցիա՝ ստուգելու, արդյոք Example կոնֆիգուրացիոն էնթիթն գոյություն ունի։
*/
public function exist($id) {
$entity = $this->entityTypeManager->getStorage('example')->getQuery()
->condition('id', $id)
->execute();
return (bool) $entity;
}
}
example/src/Controller/ExampleListBuilder.php
namespace Drupal\example\Controller;
use Drupal\Core\Config\Entity\ConfigEntityListBuilder;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
/**
* Ապահովում է Example-ի ցուցակագրում։
*/
class ExampleListBuilder extends ConfigEntityListBuilder {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function buildHeader() {
$header['label'] = $this->t('Example');
$header['id'] = $this->t('Machine name');
return $header + parent::buildHeader();
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function buildRow(EntityInterface $entity) {
$row['label'] = $entity->label();
$row['id'] = $entity->id();
// Կարելի է ավելացնել այլ հատկություններ...
return $row + parent::buildRow($entity);
}
}
example/src/Form/ExampleDeleteForm.php
namespace Drupal\example\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityConfirmFormBase;
use Drupal\Core\Url;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
/**
* Ստեղծում է ֆորմա Example-ի ջնջման համար։
*/
class ExampleDeleteForm extends EntityConfirmFormBase {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getQuestion() {
return $this->t('Are you sure you want to delete %name?', array('%name' => $this->entity->label()));
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getCancelUrl() {
return new Url('entity.example.collection');
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getConfirmText() {
return $this->t('Delete');
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$this->entity->delete();
$this->messenger()->addMessage($this->t('Entity %label has been deleted.', array('%label' => $this->entity->label())));
$form_state->setRedirectUrl($this->getCancelUrl());
}
}