9.14. Views के साथ इंटीग्रेशन लिखना
Drupal ecosystem में Views module का बहुत ज़्यादा इस्तेमाल किया जाता है। Content की lists, tables, blocks, slideshows, data export – ये सारे content के हिस्से ज़्यादातर Views के ज़रिए दिखाए जाते हैं। अगर आप Content types, Block types या किसी और Entity types का इस्तेमाल करते हैं, तो Views पहले से ही उनके साथ अपने-आप integrate हो जाता है और आप Views का इस्तेमाल करके अपना content दिखा सकते हैं। लेकिन अगर आपके custom module में आप अलग से custom database table का इस्तेमाल कर रहे हैं, जो आपने hook_schema() से बनाया है, तो आपको Views के साथ integration लिखना पड़ेगा ताकि आपके module का data Views module UI में दिख सके।
आइए देखते हैं module Did this help का Views के साथ integration:
https://www.drupal.org/project/did_this_help
यह module अपना database table बनाता है data store करने के लिए। इस table में strings, IDs, dates हैं, इसलिए हमें Views integration के लिए अलग-अलग handlers define करने होंगे:
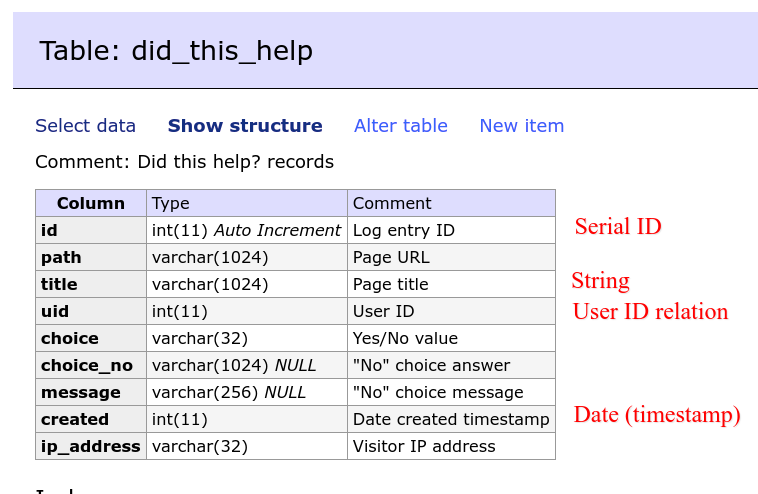
सबसे पहले आपको एक file MODULENAME.views.inc बनानी होगी, जो अपने-आप load हो जाती है, इसलिए आपको file का location कहीं और specify करने की ज़रूरत नहीं है। इस *.views.inc file में आपको hook_views_data() implement करना होगा:
<?php
/**
* @file
* Provide views data for did_this_help.module.
*/
/**
* Implements hook_views_data().
*/
function did_this_help_views_data() {
}
इस implementation के लिए आपको एक array return करना होगा जो आपके custom module के custom database table की structure को describe करे।
शुरुआत database table के नाम से करें, जो array के पहले key में होगा:
$data['did_this_help'] = [
'table' => [
'group' => t('Did this help?'),
'base' => [
'field' => 'id',
'title' => t('Did this help? entries'),
'help' => t('Contains a list of Did this help? entries.'),
],
],
];
यहां array key $data['did_this_help'] में table का description है। अगर आपको कई database tables के साथ integration करना है, तो आप $data array में अलग keys जोड़ सकते हैं: $data['did_this_help1'], $data['did_this_help2']।
इसके बाद array में 'table' description आता है:
group – UI Views में fields को एक ही partition में group करने के लिए ताकि field selection आसान हो।
base – इस table का serial ID दिखाता है। आगे जाकर हम serial ID का इस्तेमाल tables को foreign keys से जोड़ने के लिए करेंगे।
इसके बाद हम हर field को describe करेंगे, जिसे हम Views में दिखाना चाहते हैं:
$data['did_this_help']['id']= [
'real field' => 'id',
'title' => t('Did this help? record ID'),
'help' => t('Did this help? record.'),
'field' => [
'id' => 'standard',
],
'sort' => [
'id' => 'standard',
],
'filter' => [
'id' => 'numeric',
],
'argument' => [
'id' => 'numeric',
],
];
real field – असली field का नाम define करने के लिए (database table का column), अगर आप array keys में aliases का इस्तेमाल कर रहे हैं। एक Drupal field type के लिए real fields के अलग values हो सकते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए Link field के दो values होते हैं: Title और URI। हर value अपने db table column से match होती है। Column का नाम field name और property name (title, uri) से बनता है:
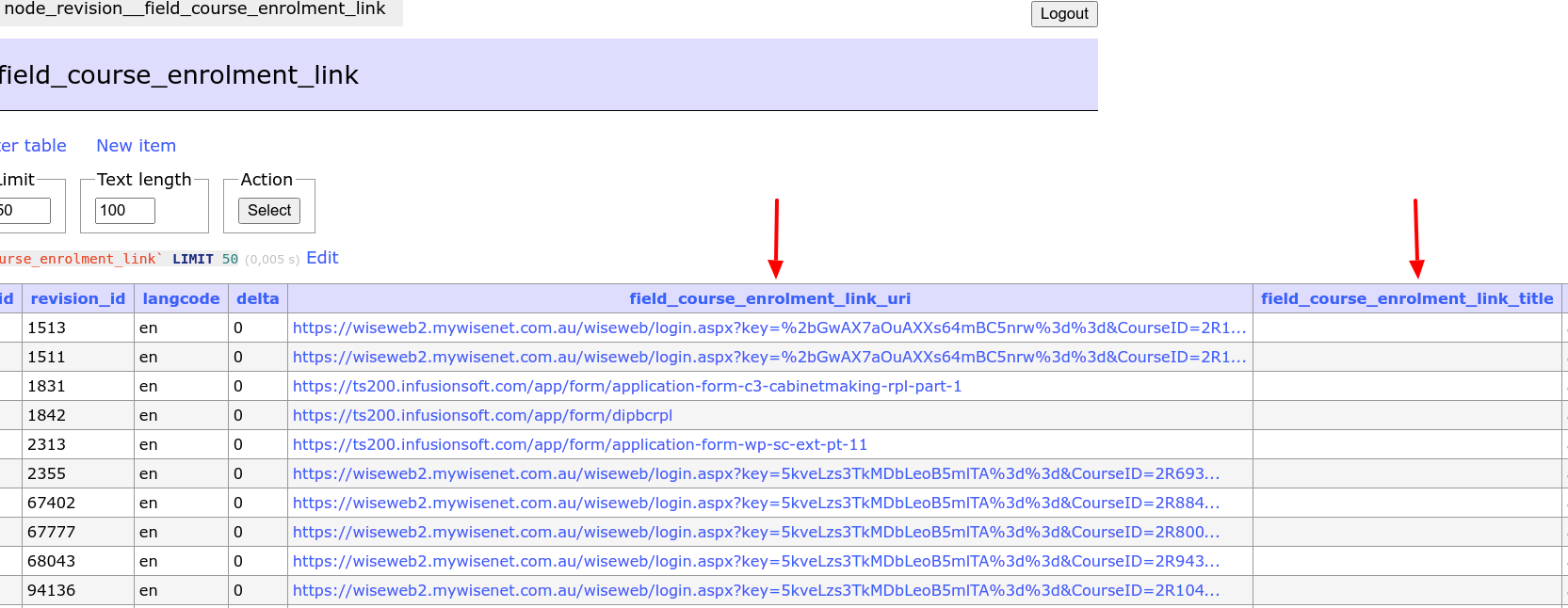
इन columns के नाम अपने-आप Link module द्वारा बनाए गए थे, लेकिन custom modules के लिए आपको hook_views_data() में अपने real field values define करने होंगे।
title, help – Views module UI के लिए जानकारी।
इसके बाद Handler IDs आते हैं: field, sort, filter, argument। Handler यह define करता है कि fields को कैसे filter और display करना है। उदाहरण के लिए dates को Date Format से display होना चाहिए और Date Calendar Popup से filter करना चाहिए। Numbers के लिए हमें filters चाहिए जिनमें operations हों >, < और =। Strings के लिए length-based filters चाहिए।
Field handlers
Field handlers SELECT word के बाद SQL query का हिस्सा generate करने में मदद करते हैं।
Drupal core से Views field handlers की list आप यहां पा सकते हैं:
Custom modules के लिए आप अक्सर numbers और strings के लिए standard handler का इस्तेमाल करेंगे, और dates के लिए आपको date handler इस्तेमाल करना चाहिए।
उदाहरण के लिए, ID field "standard" field handler का इस्तेमाल करता है:
'id' => [
'real field' => 'id',
'title' => t('Did this help? record ID'),
'help' => t('Did this help? record.'),
'field' => [
'id' => 'standard',
],
'sort' => [
'id' => 'standard',
],
'filter' => [
'id' => 'numeric',
],
'argument' => [
'id' => 'numeric',
],
],
Sort handlers
Sort handlers Views में normal sorting और exposed sorting इस्तेमाल करने में मदद करते हैं। Sort handlers SQL query के उस हिस्से को define करते हैं जो ORDER BY words के बाद आता है।
Sort handlers की list आप यहां पा सकते हैं:
Filter handlers
Filter handlers Views में normal filters, exposed filters और contextual filters दिखाने में मदद करते हैं। Filter handlers SQL query का वह हिस्सा define करते हैं जो WHERE word के बाद आता है।
Filter handlers की list आप यहां पा सकते हैं:
Dates को Date Calendar popup से filter करने के लिए आप "date" handler का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं:
$data['did_this_help']['created'] = [
'title' => t('Created date for Did this help? record'),
'help' => t('Created date for Did this help? record'),
'field' => [
'id' => 'date',
],
'argument' => [
'id' => 'date',
],
'filter' => [
'id' => 'date',
],
'sort' => [
'id' => 'date',
],
];
Relationship handler
Relationship handlers SQL query में joins जोड़ने और एक ही query में कई tables से data लाने में मदद करते हैं।
Did this help? module के DB table में user IDs वाला column है। Relationship handler का इस्तेमाल करके आप Views UI में did_this_help और users के बीच relation जोड़ सकते हैं और कई tables से data display कर सकते हैं:
$data['did_this_help']['uid'] = [
'title' => t('User ID for Did this help? record'),
'help' => t('User ID for Did this help? record'),
'field' => [
'id' => 'standard',
],
'sort' => [
'id' => 'standard',
],
'filter' => [
'id' => 'numeric',
],
'argument' => [
'id' => 'numeric',
],
'relationship' => [
'title' => t('User'),
'help' => t('The user on which the log entry as written.'),
'base' => 'users_field_data',
'base field' => 'uid',
'id' => 'standard',
],
];
इसके लिए हम field में relationship जोड़ते हैं, जहां हम "base" value specify करते हैं उस table के लिए जिसे हम join करना चाहते हैं, और "base field" specify करते हैं जिस field से join होगा; title और help Views UI के लिए; और id relationship handler। Relationship types की list आप यहां देख सकते हैं:
हालांकि, Views बहुत सारे अलग-अलग handlers provide करता है। आप किसी handler की base class को inherit करके अपना custom handler भी लिख सकते हैं field, filter, sort के लिए। अगले लेख में हम Views filter के लिए custom handler लिखेंगे।